AbigBiz > Trade Study > ArticleTrade Study
LC Letter of credit Term
![]() ABigBizJul15, 2018【Trade Study】
℃
Leave a Reply
ABigBizJul15, 2018【Trade Study】
℃
Leave a Reply
A letter of credit (LC), also known as a documentary credit, bankers commercial credit, is a payment mechanism used in international trade to perform the same economic function as a guarantee, by allocating risk undertaken by contracting parties. At law, a letter of credit is categorised within Financial law as a form of a Simple position, which alongside guarantees, derivatives, and insurance allocate risk as a form of a promise from one party to another.
A letter of credit primarily achieves this by creating a written commitment from a bank on behalf of one party that payment be made to a third-party, provided that the terms and conditions stated therein have been met. Any documents tendered which are outlined in the letter of credit, the third party will be paid by the bank.[1][2] A letter of credit is extremely common within international trade and goods delivery, where the reliability of contracting parties cannot be readily and easily determined. Its economic effect is to introduce a bank as underwriting the credit risk of the buyer paying the seller for goods.
In doing so, it plays a central role in international trade by relying upon the dependability of financial institutions and their ability to pay. Crucial to a letter of credit is the beneficiary's (the seller) attempt to isolate itself from the credit risk of the buyer. That is to say, it is concerned primarily with the ability of the buyer to pay for the goods.
Several categories of LC's exist which seek to operate in different markets and solve different issues. An example of these include:
Import/export: — The same credit can be termed an import or export letter of credit depending on whose perspective is considered. For the importer it is termed an Import LC and for the exporter of goods, an Export LC
Revocable/ Irrevocable: — Whether a LC is revocable or irrevocable determines whether the buyer and the issuing bank are able to manipulate the LC or make corrections without informing or getting permissions from the seller. According to UCP 600, all LCs are irrevocable, hence in practice this type of LC increasingly obsolete. Any changes (amendment) or cancellation of the LC (except it is expired) is done by the applicant through the issuing bank. It must be authenticated and approved by the beneficiary.
Confirmed/Unconfirmed: — An LC is said to be confirmed when a second bank adds its confirmation (or guarantee) to honor a complying presentation at the request or authorization of the issuing bank.
Restricted/ Unrestricted: — Either the one advising bank can purchase a bill of exchange from the seller in the case of a restricted LC or; the confirmation bank is not specified, which means that the exporter can show the bill of exchange to any bank and receive a payment on an unrestricted LC.
Deferred / Usance: — A credit that is not paid/assigned immediately after presentation, but after an indicated period that is accepted by both buyer and seller. Typically, seller allows buyer to pay the required money after taking the related goods and selling them.
Additionally, a letter of credit may also have specific terms relating to the payment conditions which relate to the underlying reference documents. Some of these include
At Sight: — A credit that the announcer bank immediately pays after inspecting the carriage documents from the seller.
Red Clause: — Before sending the products, seller can take the pre-paid part of the money from the bank. The first part of the credit is to attract the attention of the accepting bank. The first time the credit is established by the assigner bank, is to gain the attention of the offered bank. The terms and conditions were typically written in red ink, thus the name.
Back to Back: — A pair of LCs in which one is to the benefit of a seller who is not able to provide the corresponding goods for unspecified reasons. In that event, a second credit is opened for another seller to provide the desired goods. Back-to-back is issued to facilitate intermediary trade. Intermediate companies such as trading houses are sometimes required to open LCs for a supplier and receive Export LCs from buyer.
Standby Letter of Credit: — Operates like a Commercial Letter of Credit, except that typically it is retained as a "standby" instead of being the intended payment mechanism. In other words, this is a LC which is intended to provide a source of payment in the event of non-performance of contract. This is a security against an obligation which is not performed. If you present the bank with demands of non-payment it is not a guarantee - trigger isn't non-payment - it is presented by documentation.[9] UCP600 article 1 provides that the UCP applies to Standbys; ISP98 applies specifically to Standby letters of Credit; and the United Nations Convention on Independent Guarantees and Standby Letters of Credit applies to a small number of countries that have ratified the Convention.
A letter of credit primarily achieves this by creating a written commitment from a bank on behalf of one party that payment be made to a third-party, provided that the terms and conditions stated therein have been met. Any documents tendered which are outlined in the letter of credit, the third party will be paid by the bank.[1][2] A letter of credit is extremely common within international trade and goods delivery, where the reliability of contracting parties cannot be readily and easily determined. Its economic effect is to introduce a bank as underwriting the credit risk of the buyer paying the seller for goods.
In doing so, it plays a central role in international trade by relying upon the dependability of financial institutions and their ability to pay. Crucial to a letter of credit is the beneficiary's (the seller) attempt to isolate itself from the credit risk of the buyer. That is to say, it is concerned primarily with the ability of the buyer to pay for the goods.
Several categories of LC's exist which seek to operate in different markets and solve different issues. An example of these include:
Import/export: — The same credit can be termed an import or export letter of credit depending on whose perspective is considered. For the importer it is termed an Import LC and for the exporter of goods, an Export LC
Revocable/ Irrevocable: — Whether a LC is revocable or irrevocable determines whether the buyer and the issuing bank are able to manipulate the LC or make corrections without informing or getting permissions from the seller. According to UCP 600, all LCs are irrevocable, hence in practice this type of LC increasingly obsolete. Any changes (amendment) or cancellation of the LC (except it is expired) is done by the applicant through the issuing bank. It must be authenticated and approved by the beneficiary.
Confirmed/Unconfirmed: — An LC is said to be confirmed when a second bank adds its confirmation (or guarantee) to honor a complying presentation at the request or authorization of the issuing bank.
Restricted/ Unrestricted: — Either the one advising bank can purchase a bill of exchange from the seller in the case of a restricted LC or; the confirmation bank is not specified, which means that the exporter can show the bill of exchange to any bank and receive a payment on an unrestricted LC.
Deferred / Usance: — A credit that is not paid/assigned immediately after presentation, but after an indicated period that is accepted by both buyer and seller. Typically, seller allows buyer to pay the required money after taking the related goods and selling them.
Additionally, a letter of credit may also have specific terms relating to the payment conditions which relate to the underlying reference documents. Some of these include
At Sight: — A credit that the announcer bank immediately pays after inspecting the carriage documents from the seller.
Red Clause: — Before sending the products, seller can take the pre-paid part of the money from the bank. The first part of the credit is to attract the attention of the accepting bank. The first time the credit is established by the assigner bank, is to gain the attention of the offered bank. The terms and conditions were typically written in red ink, thus the name.
Back to Back: — A pair of LCs in which one is to the benefit of a seller who is not able to provide the corresponding goods for unspecified reasons. In that event, a second credit is opened for another seller to provide the desired goods. Back-to-back is issued to facilitate intermediary trade. Intermediate companies such as trading houses are sometimes required to open LCs for a supplier and receive Export LCs from buyer.
Standby Letter of Credit: — Operates like a Commercial Letter of Credit, except that typically it is retained as a "standby" instead of being the intended payment mechanism. In other words, this is a LC which is intended to provide a source of payment in the event of non-performance of contract. This is a security against an obligation which is not performed. If you present the bank with demands of non-payment it is not a guarantee - trigger isn't non-payment - it is presented by documentation.[9] UCP600 article 1 provides that the UCP applies to Standbys; ISP98 applies specifically to Standby letters of Credit; and the United Nations Convention on Independent Guarantees and Standby Letters of Credit applies to a small number of countries that have ratified the Convention.
- END -
Finished browsing? You can ask me to comment and Leave a Reply!
Leave a Reply!
Prev:Unfind
Next:FOB-Free On Board
Other articles
- An award winning B2B vision 2015
- The bright future of trading
- Ebola Virus Reduces Import of Bauxite
- Foreigners Understand Jay Chou's Song?
- The Excruciating Oversea Locations
- 6 reasons why every time B2B and B2C
- How to Know Your Product?
- How to select B2B industry site Management System
- Key points of being a successful salesman
- Analysis of Australian Market
Related news
Notes of doing business with Indian
Notes of doing business with Indian According to customs statistics, our main pro...The bright future of trading
In 15th July, the Commerce Department held a pre-match press conference to announ...The strategy for the B2B website keywords SEO
About keyword strategy of the complexity and than a few areas and b2b e-commerce ...How to Improve your Export Ability
Export Ability Product is the keypoint of foreign trade . From the ancient to now...
Leave a Reply
- 全部评论(0)

说点什么吧
还没有评论,快来抢沙发吧!
Popular this month
 The best communication time
The best communication timeRecommended

As for the foreign trader, we usually need to negotiate and communicate with the ...
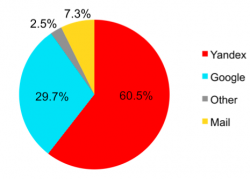
Russian market has been a big chance for foreign trade salesmen because in recent...

Hello everyone! Today I would like to introduce some useful and daily apps in Ind...

As we all know, the hot products play an important part in the development of a s...
Tags
You love
- 10 Sentences That Will Make You Smile
- How to Maintain Your Old Customers?
- Tips for Final Fighting in 2016
- How to Write Claim Letters
- I Was Just the Tool
- What Are You Going to Ask
- Analysis Helps You Win Order!
- What's Wrong With Your Quotation?
- African nations may be the new Brics
- Unfathomable Foreign Trade




 微信扫码打赏
微信扫码打赏 支付宝收款码
支付宝收款码